
What Is the 30% Rule for AI
The 30% Rule for AI is a practical framework that guides organizations to use artificial intelligence for approximately one-third of their workflows, while preserving human control over the remaining majority of decisions and operations. Instead of replacing people, AI is used to enhance productivity, accelerate execution, and support informed decision-making. This approach improves efficiency, reduces operational risk, and ensures that human judgment, ethics, and creativity remain central to organizational performance.
What Is the 30% Rule for AI?
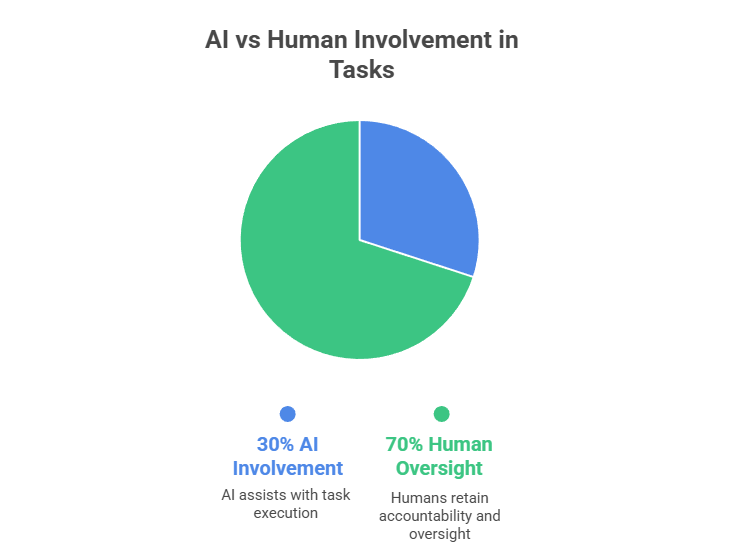
The 30% Rule for AI is a governance-driven principle that encourages organizations to rely on AI for around 30% of task execution, automation, and data-driven activities. The remaining 70% continues to depend on human oversight, strategic thinking, contextual understanding, and ethical responsibility. This balance ensures that AI functions as a supportive capability rather than a full replacement for human intelligence.
The rule emphasizes responsible AI adoption by positioning technology as a collaborative asset that assists with repetitive, analytical, or process-based work. Human teams retain accountability for approvals, decision-making, creativity, and stakeholder communication. By applying the 30% balance, organizations strengthen performance while maintaining quality control, trust, and operational resilience.
How the 30% Rule for AI Works
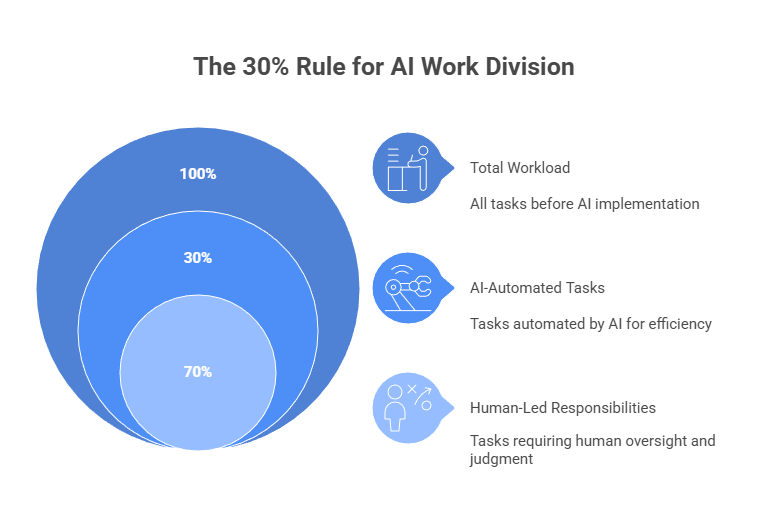
The 30% Rule operates by dividing work between automation-ready tasks and human-led responsibilities. AI is applied where it improves efficiency and speed, while humans remain responsible for strategic, ethical, and judgment-based activities. This structured division ensures that productivity gains do not come at the expense of accuracy, quality, or accountability.
1. Automating Repetitive and Low-Value Tasks
The rule prioritizes AI for activities such as data entry, formatting, content drafting, scheduling, and workflow preparation. These tasks consume time but deliver limited strategic value, making them ideal for automation support. By assigning such activities to AI, organizations free human teams to focus on higher-impact initiatives and creative problem-solving.
2. Maintaining Human Oversight for Critical Work
High-impact activities such as approvals, decision-making, client communication, policy evaluation, and ethical review remain human-controlled because these areas require context awareness, accountability, empathy, and strategic insight that automation alone cannot replicate. This need for human involvement is reinforced by survey data showing that 93% of business leaders believe humans should be involved in AI decision-making, especially for significant or sensitive outcomes, highlighting widespread concern about automated decisions without human oversight.
3. Using AI as a Productivity Multiplier
Rather than replacing workers, AI assists teams in working faster and more efficiently while retaining ownership of results. It accelerates research, analysis, drafting, and administrative execution, allowing professionals to redirect time toward innovation and decision-driven responsibilities. This creates a collaborative human-AI operating model that enhances performance and capability.
Keep Human Oversight for High-Impact Work
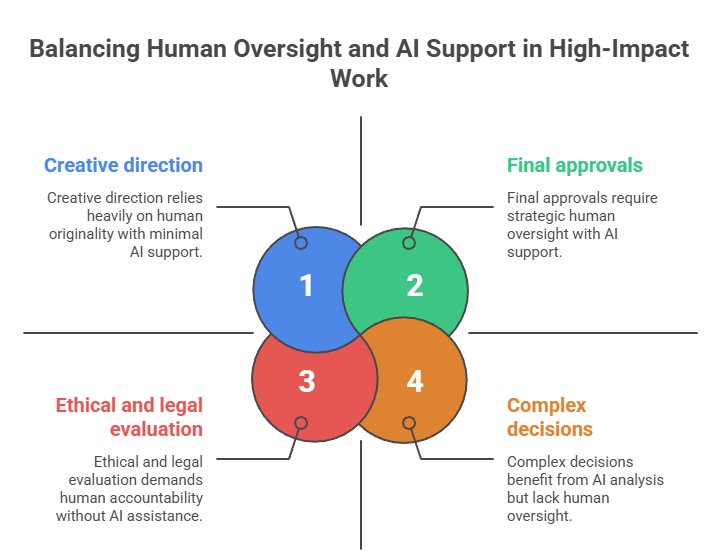
Humans remain responsible for high-impact work because these activities require context, accountability, emotional intelligence, and strategic judgment that AI cannot replicate. Decisions in these areas affect customers, brand trust, compliance, and long-term business outcomes, meaning they must be evaluated by people who understand nuance and real-world implications. In this model, AI functions as an assistant that informs decisions rather than a system that replaces human authority.
1. Final approvals
Final approvals remain human-led to ensure every outcome is reviewed with strategic awareness, ethical consideration, and organizational alignment. Leaders evaluate risks, implications, and stakeholder expectations before sign-off, preventing automation from making unchecked or irreversible decisions. This oversight protects quality, accountability, and decision integrity across business processes.
2. Creative direction
Creative direction requires originality, brand personality, emotional tone, and conceptual thinking that AI cannot fully imitate. Humans shape messaging, storytelling, campaign vision, and creative identity to maintain authenticity and differentiation in the marketplace. AI may assist with drafts or ideas, but human leaders guide the final narrative and expression.
3. Client communication
Client communication involves relationship management, trust-building, persuasion, and empathy that depend on human judgment and conversational awareness. Professionals interpret tone, concerns, and expectations in ways AI cannot fully understand or respond to appropriately. By keeping humans at the center, organizations maintain credibility and meaningful client engagement.
4. Complex decisions
Complex decisions require strategic reasoning, scenario evaluation, ethical balance, and insight into business impact beyond raw data. Human leaders synthesize multiple variables, including uncertainty, risk, and long-term implications that AI cannot assess independently. AI may support analysis, but humans ultimately decide direction and responsibility.
5. Ethical and legal evaluation
Ethical and legal evaluation demands accountability, regulatory understanding, moral reasoning, and societal awareness that automated systems do not possess. Humans assess fairness, compliance risk, privacy impact, and social responsibility before actions are executed. This ensures decisions remain defensible, transparent, and aligned with legal and ethical standards.
6. AI becomes a support tool, not the decision-maker
Within this framework, AI provides insights, summaries, recommendations, and operational support while humans retain control of judgment-driven outcomes. The technology enhances efficiency and visibility but does not replace leadership, responsibility, or final authority. This balance ensures organizations benefit from AI while preserving trust, accountability, and strategic control.
Key Applications of the 30% Rule for AI
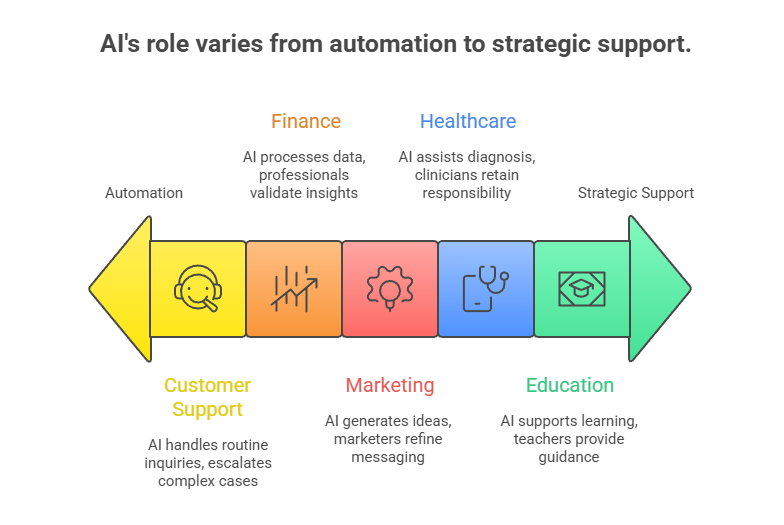
The 30% Rule adapts successfully across multiple industries by assigning AI to automation-ready tasks while preserving human oversight for strategic, ethical, and judgment-driven responsibilities. Organizations apply the guideline differently based on operational risk, compliance needs, and organizational priorities, allowing AI to support productivity without diminishing human authority or accountability.
1. Marketing
AI assists with idea generation, audience insights, data analysis, and first-draft content development, helping teams accelerate creative workflows and campaign preparation. Human marketers refine messaging, brand tone, narrative direction, and strategic positioning to ensure authenticity and originality remain intact. This balance allows organizations to improve content efficiency while protecting creativity and brand identity.
2. Customer Support
AI manages FAQs, ticket triage, initial inquiries, and routine messaging to enhance service speed and availability across support channels. Sensitive, complex, or emotionally driven cases are escalated to human agents who apply empathy, interpretation, and relationship-based communication. This approach strengthens customer trust while reducing operational burden.
3. Finance and Data Operations
AI processes large datasets, identifies trends, produces summaries, and supports forecasting to improve analytical efficiency and data visibility. Financial professionals review outputs, test assumptions, validate insights, and make final risk-based decisions that require judgment and accountability. This collaboration preserves analytical integrity and decision reliability.
4. Healthcare
AI assists with diagnostic support, pattern recognition, clinical data processing, and research analysis to help physicians access timely insights, and clinicians retain full responsibility for medical judgment, treatment planning, patient communication, and ethical decision-making. According to a 2025 survey, 66% of U.S. physicians reported using AI tools in clinical practice, yet most still emphasize that human interpretation and oversight remain essential for safe patient care and complex decision-making, reinforcing that technology augments rather than replaces clinical judgment.
5. Education
AI enhances learning experiences through research support, practice activities, adaptive feedback, and academic reinforcement tools that assist students and educators. Teachers provide interpretation, contextual explanation, mentorship, and critical-thinking guidance to shape meaningful intellectual development. This balance strengthens learning outcomes while keeping human instruction at the core of education.
Benefits of Following the 30% Rule for AI
The 30% Rule delivers measurable organizational value by balancing automation with human oversight. It supports productivity growth while safeguarding decision quality, ethics, and operational reliability.
1. Higher Accuracy and Reliability
Human review ensures AI-generated outputs are verified, preventing misinformation, bias errors, or contextual misalignment in decision processes.
2. Stronger Ethics and Compliance
By retaining human authority in sensitive areas, organizations maintain accountability, transparency, and regulatory alignment across AI-enabled workflows.
3. Improved Creativity and Critical Thinking
AI reduces administrative workload, allowing professionals to focus on innovation, reasoning, and strategic problem-solving instead of repetitive execution.
4. Sustainable AI Adoption
Gradual, balanced implementation reduces workforce disruption and promotes organizational trust, enabling long-term transformation rather than risky over-automation.
5. Balanced Productivity
AI accelerates execution while humans preserve meaning, context, and quality across outcomes, creating a scalable and resilient productivity model.
Risks of Ignoring the 30% Rule
Organizations that over-automate without safeguards face increased operational and reputational risk. The 30% Rule acts as a protective boundary to prevent unintended consequences.
1. Misinformation and Hallucinations
Unverified AI outputs may introduce errors or fabricated information into workflows, leading to flawed decisions and inaccurate conclusions.
2. Compliance and Legal Exposure
Automation without oversight may bypass regulatory or ethical considerations, increasing risk of violations, disputes, and policy misalignment.
3. Decline in Customer Experience
Excessive automation can create rigid, impersonal interactions, weakening trust and diminishing human connection in service environments.
4. Erosion of Organizational Trust
Stakeholders lose confidence when decisions appear overly machine-dependent or lack human accountability and transparency.
5. Reduced Skill Development
Over-reliance on AI may weaken critical thinking and professional expertise within teams, reducing long-term institutional capability.
TaskVirtual: Your Partner in Online Assistance Services
The 30% Rule for AI highlights the importance of balancing automation with skilled human support, ensuring that technology enhances productivity without replacing human judgment. TaskVirtual strengthens this balance by providing professional virtual assistant services where precision, coordination, and contextual decision-making are essential. Their services complement AI-enabled operations by managing tasks that require reliability, organization, and hands-on oversight, helping organizations apply the Rule for AI effectively in real-world workflows.
1. Expert Consultation and Review
TaskVirtual’s experienced virtual assistants help organize workflows, coordinate digital activities, and manage recurring tasks with accuracy and consistency. They support scheduling, platform navigation, follow-ups, and operational review to ensure smooth execution beyond automated outputs.
2. Affordable and Flexible Pricing
Instead of hiring full-time administrative staff, organizations benefit from cost-efficient support plans ranging from $3.12/hour to $14.99/hour. This flexible pricing model allows users to scale assistance based on workload and operational requirements.
3. Comprehensive Task Support Solutions
TaskVirtual delivers end-to-end assistance for online coordination, subscriptions, service management, reminders, tracking, and digital process handling. Their services adapt seamlessly to both short-term and ongoing support needs.
4. Ongoing Support and Quality Assurance
Beyond execution, TaskVirtual emphasizes continual monitoring, updates, reminders, and validation checks. This proactive approach ensures reliability, timeliness, and quality across every managed activity.
5. Proven Track Record of Excellence
With 364 verified reviews and a 4.7-star service rating, TaskVirtual is recognized globally as a trustworthy partner for operational assistance, productivity support, and process coordination.
Is the 30% Rule a Law or Policy?
The 30% Rule for AI is not a formal law or regulatory requirement; instead, it functions as a best-practice guideline adopted by organizations, consultants, and technology governance teams to promote responsible and balanced AI adoption. It serves as a strategic principle rather than a mandated policy, helping businesses use AI in a controlled and ethical manner while maintaining human oversight in critical areas of work. Different industries and organizations may adapt or modify the guideline based on their operational needs, risk tolerance, and regulatory environment, which makes the 30% Rule flexible rather than prescriptive.
Final Thoughts on the 30% Rule for AI
The 30% Rule for AI provides a disciplined framework for achieving efficiency through automation while preserving human judgment, accountability, and ethical oversight. By positioning AI as a collaborative productivity partner rather than a replacement technology, organizations strengthen decision quality, trust, and operational sustainability. When complemented with skilled human support solutions such as TaskVirtual, businesses achieve a balanced, scalable, and responsible approach to modern productivity and digital operations.
FAQ: The 30% Rule for AI
1. What is the 30% Rule for AI?
It is a guideline recommending that AI should support around 30% of tasks, while the remaining majority stays human-led to preserve oversight, ethics, and judgment.
2. Is the 30% Rule legally required?
No — it is a best-practice framework used to guide responsible and sustainable AI adoption.
3. Can organizations adjust the percentage?
Yes — the ratio may vary by industry, workload, or risk tolerance, typically ranging between 20% and 40%.
4. Does this rule apply to personal productivity?
Yes — individuals can use AI for drafting, research, and planning while keeping decisions and interpretation human-controlled.
5. Is the 30% Rule still relevant in the future?
Yes — as AI becomes more powerful, structured oversight remains essential for safety, accountability, and responsible adoption.








